An Antibody, Or Immunoglobulin, Is A Type Of Glycoprotein Made By Plasma Cells
 |
| Immunoglobulin |
The science behind Immunoglobulin revolves around understanding the structure,
function, and production of these vital components of the immune system.
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, play a crucial role in defending the
body against invading pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This
article aims to provide an overview of the science behind immunoglobulin,
shedding light on its importance and the mechanisms through which it protects
our health.
Immunoglobulin are proteins produced by specialized white blood cells called B cells or
B lymphocytes. These proteins are part of the humoral immune response, which is
one of the two main branches of the immune system. The other branch is the
cell-mediated immune response, involving T cells. Immunoglobulins are secreted
or membrane-bound molecules that recognize and neutralize specific foreign
substances known as antigens.
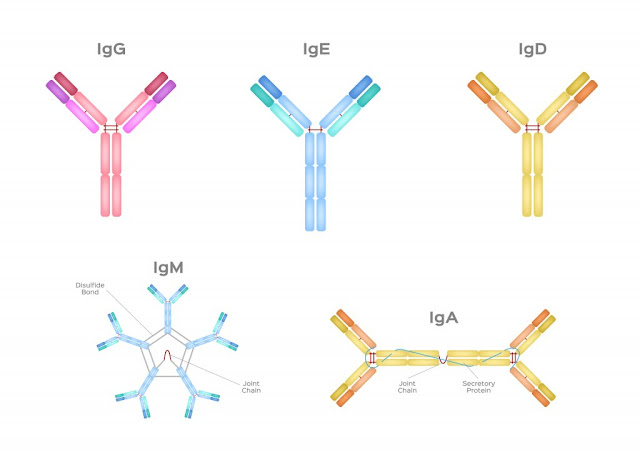
The basic structure of an immunoglobulin molecule consists of
two heavy chains and two light chains, forming a Y-shaped structure. The heavy
and light chains are held together by disulfide bonds. The variable regions of
the chains, also known as antigen-binding sites, are responsible for
recognizing and binding to specific antigens. This unique feature allows Immunoglobulins to target a wide range
of pathogens with high specificity.
Your immune system creates defensive proteins called Antibodies. They bind to antigens
(foreign substances), which include poisons, viruses, bacteria, and fungus, and
eliminate them from your body. Proteins called Antibodies
defend you when your body comes into contact with an unwelcome chemical.
Antibodies, which are made by your immune system, bind to these foreign
chemicals and drive them out of your body. Immunoglobulin
is another name for an antibody.
There are five major classes of immunoglobulins, known as IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD. Each class
has distinct properties and functions. IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin
in the bloodstream and provides long-term protection by neutralizing toxins and
enhancing phagocytosis. IgA is found predominantly in mucosal areas, such as
the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, where it acts as the first line of
defense against pathogens. IgM is the first immunoglobulin produced during an
infection and is associated with the primary immune response. IgE is involved
in allergic reactions and defense against parasites. IgD has a role in
activating B cells.



Comments
Post a Comment