Microfluidics; a Form of Laboratory Technology That Enables Researchers to Work with a Reduced Sample Size at Lower Cost
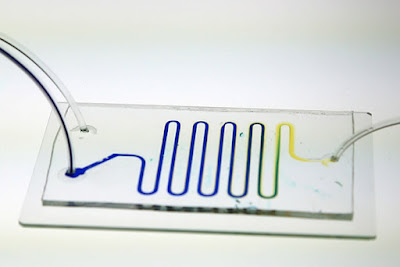 |
| Microfluidics |
Microfluidics
involves the manipulation of fluids at the microscale. It is a form of
laboratory technology that enables scientists to work with a reduced sample
size and at lower cost. As a result, scientists can conduct experiments with a
higher degree of confidence and a reduced limit of detection. For example, when
conducting a study, a scientist can perform a high throughput cell culture with
a microfluidic lab-on-a-chip. This form of technology can be used to study
single cell behavior, intercellular communication, and cell locomotion. These
results are comparable to macroscopic culture assays.
When
working with a Microfluidics
lab-on-a-chip, a scientist must consider several factors in order to make
effective use of the system. One of the main considerations is the type of
material used for the chip. Many devices are made of polymer, such as PDMS
(polydimethylsiloxane). The material can be transparent and easy to bond to
glass. Moreover, it is highly permeable to gases. Another consideration is the
relative pressure in the chip. If the chips are made of PDMS, a relative
pressure of about two Bars should be maintained. However, if the chips are made
of thermoplastic, the relative pressure may be increased by as much as 10 Bars.
For
the same reason, it is important to design the Microfluidics channels with a constant depth. Changing the depth
should be done in a step-wise manner. A change in depth can affect the gas
exchange and the turbulence of the fluid.
Microfluidics
devices also allow for rapid drug changes. The device can be used for sorting,
mixing, and pumping. Also, it can be used to monitor a variety of biochemical
environments. They have a dual channel configuration, which reduces the
variation in experimental results. Microfluidic devices can be made of several
materials, including PDMS, glass, and silicon. Each of these materials is able
to be shaped, which means it can be fabricated into various shapes. Some of
these microfluidic components are molded, while others are manufactured with a
DRIE process. In November 2022, LumiraDx announced the launch of Rapid
Microfluidic Immunoassay C-Reactive Protein Test for helping combat
Antimicrobial Resistance in India.



Comments
Post a Comment