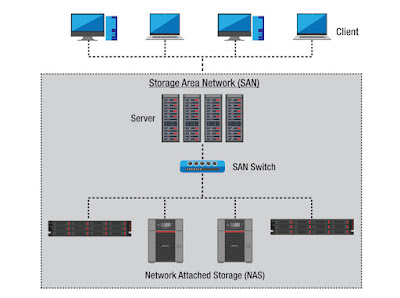
Storage Area Network (SAN); a Dedicated Network of Storage Devices Used To Provide A Pool of Shared Storage
 |
| Storage Area Network |
Storage Area Network (SAN) is a
specialized, high-speed network that provides network access to storage
devices. SAN is a network of storage devices that can be accessed by multiple
servers or computers, providing a shared pool of storage space. Each computer
can access storage on the SAN as though they were local disks connected
directly to the computer. A SAN allows us to combine many file-systems into a
single disk array, allowing far more efficient use of storage resources.
Because SAN is block level, it is able to do this anytime that a traditional,
local disk subsystem could be employed.
Storage
Area Network is a modular computer
network that provides centralized, file-level access to multiple, fixed-size
block storage. It is a dedicated, independent network that interconnects and
distributes a shared pool of storage devices to multiple servers. It is mostly
used to access large data storage devices, including tape libraries and disk
arrays, from multiple servers, so that devices appear as if they are directly connected
to the operating system. SAN also includes a management layer that organizes
the connections, storage elements, and computer systems.
This layer ensures secure and robust data
transfers. Storage Area Network (SAN) typically is a dedicated network of
storage devices not accessible through local area network (LAN). Most people
are familiar with a traditional local area network, in which every computer
connects to every other computer on the LAN. With SAN, however, each computer
is connected only to its own storage area. This means that each computer on the
network does not need to connect to other computers on the LAN, which can save
space and money.
Storage Area Network (SAN) benefits include
speed, scalability and fault tolerance, and have become increasingly popular
over the years. As a result, there is an increasing demand for SAN worldwide,
especially in the U.S., Germany, Japan, Mexico, and India.



Comments
Post a Comment